
Introduction
eCommerce businesses need a powerful architecture to ensure smooth operations and efficient website performance. And you can either go for monolithic or MACH architecture to develop the eCommerce store.
The choice of architecture depends on different factors, such as the complexity of the requirements, scalability needs, development team expertise, long-term goals, budget, performance optimization, integration requirements, and the ability to embrace new technologies.
This is a Monolith to MACH series of 4 informative articles, each explaining different components of the MACH architecture – Microservices-based, API-first, Cloud-native, and Headless architecture. Read on…
First, let’s understand the difference between monolithic and MACH architecture.
Monolithic Vs. MACH Architecture
Monolithic Architecture
Monolithic architecture for eCommerce refers to a traditional approach where the entire eCommerce application is built as a single, unified system. All components, including the frontend, backend, and database, are tightly coupled and packaged together as a single deployable unit.
Pros
- Monolithic architecture is relatively easier to develop, deploy, and manage as all components fall under a single codebase.
- Communication between components within the monolith is usually fast, resulting in efficient performance.
Cons
- Scaling individual components or introducing new technologies can be challenging due to the tight coupling of components in a monolithic architecture.
MACH Architecture
MACH architecture stands for Microservices, API-first, Cloud-native, and Headless. It offers a more modular and decoupled approach to eCommerce application development.
- Microservices are the smaller, loosely coupled services that make up the entire eCommerce system.
- The API-first principle focuses on designing and exposing well-defined APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for the various services in the eCommerce architecture. These APIs enable seamless communication and integration between different components, both internally and with external systems.
- Cloud-native architecture leverages cloud computing platforms and services to build and deploy eCommerce applications. It involves utilizing the scalability, reliability, and flexibility provided by cloud infrastructure, such as auto-scaling, containerization (using technologies like Docker), and orchestration (using tools like Kubernetes). Consequently, it enables rapid deployment of eCommerce systems.
- The headless principle separates the frontend presentation layer from the backend business logic. In a headless architecture, the frontend (head) is decoupled from the backend and communicates with it through APIs.
Pros
- MACH architecture’s microservices approach allows for horizontal scalability, where individual services can be scaled independently based on demand, making it more suitable for handling high-traffic loads.
- Each eCommerce functionality can be developed and updated independently, leading to greater flexibility in adopting new technologies, frameworks, or third-party services.
- MACH architecture enables faster development cycles and the ability to introduce new features or update existing ones with reduced impact on the overall system.
- The headless approach in MACH architecture allows the frontend to be decoupled from the backend, enabling flexibility in delivering content and experiences across different channels and devices.
Cons
- MACH architecture introduces additional complexity compared to monolithic architecture due to managing and coordinating multiple microservices.
- Building and managing distributed systems come with challenges like service discovery, inter-service communication, data consistency, and network latency.
- Orchestrating and maintaining multiple services in MACH architecture can require additional effort in terms of deployment, monitoring, and debugging.
Now that we know the differences between the two architectures, let’s discuss what APIs are.
What are APIs?
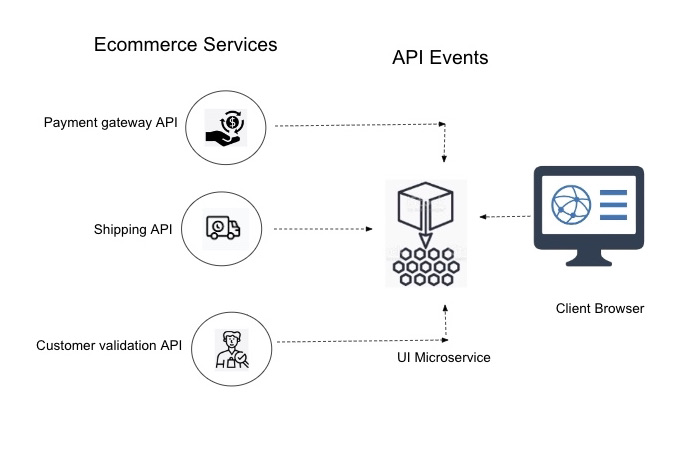
APIs play a crucial role in enabling communication and integration between the various components and services. Consider the example of a delivery executive who goes to the store or warehouse and brings you the order.
Here are the most popular APIs used in the MACH architecture.
1. Service APIs
Service APIs are the APIs exposed by individual microservices in the eCommerce system. Each microservice provides well-defined APIs that allow other services or components to interact with its specific functionality. Service APIs enable communication between different microservices, facilitating the modular and independent development, deployment, and scaling of services within the architecture.
2. Commerce APIs
Commerce APIs provide access to eCommerce-specific functionalities, such as product catalogs, pricing, inventory management, shopping carts, and checkout processes. These APIs allow external systems or frontend applications to retrieve or update eCommerce data and perform transactions. Commerce APIs enable integrations with third-party systems, such as payment gateways, shipping providers, or marketing tools.
3. Content APIs
Content APIs are used to manage and deliver content in the headless architecture. They allow frontend applications to retrieve content, such as product descriptions, images, blog posts, or marketing banners, from a content management system (CMS) or digital experience platform (DXP). Content APIs enable content personalization, localization, and delivery across various channels.
4. Integration APIs
Integration APIs help in communication and data exchange between the eCommerce system and external systems or services. They enable integration with third-party applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, analytics platforms, or marketing automation tools. Integration APIs enable data synchronization, event notifications, and seamless collaboration with external systems.
5. Third-Party APIs
In addition to the APIs within the MACH architecture, third-party APIs are often utilized to leverage external services or functionalities. These can include payment gateways, shipping carriers, social media platforms, geolocation services, or other specialized services that complement the eCommerce offering. Third-party APIs expand the capabilities of the eCommerce system and enable seamless integration with external services.
Besides these, there are two more approaches to implementing APIs – open and private APIs.
- Open APIs
Open APIs, also known as public APIs, are designed to be accessible to external developers, partners, or third-party applications. They are made available to the public and can be used by anyone who registers for an API key or meets certain authentication requirements. Open APIs are typically documented, well-defined, and follow industry standards to ensure ease of use and interoperability. They enable developers to build applications, services, or integrations that interact with the exposed functionality of the API provider. Open APIs foster innovation, collaboration, and the creation of ecosystem-driven solutions.
- Private APIs
Private APIs, also called internal APIs or partner APIs, are designed for specific use within an organization or restricted to a limited group of trusted partners. They are not publicly accessible and require authentication or authorization to access. Private APIs are often used for internal systems integration, enabling different applications or services within an organization to communicate and share data securely. They provide a controlled and secure way to expose functionality or data to selected stakeholders while maintaining privacy and security measures. Private APIs are not typically intended for external public use.
How eCommerce Models Guide the Choice of APIs and Data Ochestration
Your eCommerce model plays an integral part in guiding the choice of APIs and data orchestration strategies. The specific requirements and characteristics of each eCommerce model influence the selection of appropriate APIs and the way data is orchestrated within the system. Here’s how different eCommerce models can guide these choices:
- Commerce-first Model
In the commerce-first model, you have an eCommerce platform on the frontend for the user experience and checkout. The backend uses APIs for data orchestration with an ERP, PIM, OMS, or other system. This strategy utilizes highly-extensible SaaS technologies.
- Experience-first Model
The experience-first approach, also known as the headless commerce model, decouples the presentation layer from the eCommerce platform and uses popular CMS like WordPress. API connectivity is crucial for proper data orchestration in decoupled systems. This model prioritizes attracting customers by delivering pleasant content experiences. Through this approach, you can use the API economy to make use of the best applications at the presentation layer to address the challenges unique to your business.
Influence of APIs on eCommerce Tech Stack
APIs have a significant influence on various aspects of an eCommerce tech stack, including flexibility, security, reusability, scalability, and extensibility. Here’s a breakdown of how APIs impact each of these factors:
- Flexibility
With well-designed and documented APIs, businesses can easily connect their eCommerce platform with third-party services such as payment gateways, shipping providers, marketing tools, or social media platforms. This flexibility allows businesses to adopt best-of-breed solutions, leverage specialized services, and adapt to changing business needs without the need for extensive customization or redevelopment.
- Security
APIs play a crucial role in maintaining security in an eCommerce tech stack. APIs provide controlled access to data and functionality, allowing businesses to implement authentication, authorization, and encryption mechanisms to secure communication and protect sensitive customer and business information. By adhering to security best practices, such as using secure protocols (HTTPS), implementing API keys or tokens, and applying rate limiting, businesses can ensure secure interactions between their eCommerce platform and external systems.
- Reusability
By exposing well-defined APIs, different components or services within the tech stack can be designed to interact with each other in a modular and reusable manner. For example, an inventory management API can be reused by multiple modules or applications within the eCommerce platform, ensuring consistent and efficient inventory management across different processes. API-driven reusability reduces redundancy, promotes consistency, and simplifies maintenance and updates across the tech stack.
- Scalability
APIs enable horizontal or vertical scaling of individual components or services. With properly designed APIs, businesses can scale specific functionalities independently based on demand or resource requirements. For example, by scaling the order processing API separately from the product catalog API, businesses can handle increased order volume without affecting the availability or performance of other components. APIs allow businesses to distribute the load, balance resources, and scale different parts of the tech stack efficiently.
- Extensibility
Businesses can offer integration points for developers or partners to extend the capabilities of the eCommerce platform with the help of APIs. These extensions can range from custom integrations with external systems, adding new features or building specialized modules to meet specific business requirements. APIs enable businesses to build an ecosystem of extensions, plugins, or integrations that enhance the functionality and adaptability of the eCommerce tech stack.
If you want to explore a true futuristic eCommerce platform, here is one that we vouch for:
Commercetools is an API-first platform, meaning that all its functionalities are accessible through well-documented APIs. This enables seamless integration with external systems, third-party services, and custom applications. Businesses can create custom storefronts, leverage modern frontend frameworks, and craft personalized customer experiences with ease.
Wrapping Up
By leveraging APIs effectively, businesses can create effective eCommerce systems that adapt to evolving requirements, integrate with external services, and render personalized user experiences. Careful API design, documentation, and implementation are crucial to emerge as a winner in the competitive bottleneck of the eCommerce industry.

As Director - Marketing, Zenul leads the marketing and branding at Krish. He brings with him an in-depth understanding of the evolving digital ecosystem and has a proven expertise and experience in strategic planning, market and competition analysis, creating and implementing client-centered, lead-gen and brand marketing campaigns. He has a heart for technology innovation and has been a keynote speaker on various platforms.
Recommended Reading:
commercetools Composable Commerce for B2B Success
15 February, 2024 In the ever-evolving landscape of B2B eCommerce, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for businesses aiming for sustained growth and success. In 2023, the rise of B2B eCommerce has been nothing short of revolutionary, with businesses embracing innovative solutions to streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive revenue. One such groundbreaking approach gaining traction is Composable Commerce, a strategy that empowers businesses to assemble and orchestrate their commerce stack to meet specific business needs. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of Composable Commerce for B2B businesses and delve into why commercetools emerges as the go-to platform for unleashing its full potential.
Subscribe with Us!
Never miss any post, stay tuned!
Trusted by leading brands




